Competitive Effects of Oxidation and Quantum Confinement on Modulati…
페이지 정보
본문
| 논문명 | Competitive Effects of Oxidation and Quantum Confinement on Modulation of the Photophysical Properties of Metallic-Phase Tungsten Dichalcogenide Quantum Dots |
|---|---|
| 저자 | Bo-Hyun Kim, Jun Yong Yan, Kwang Hyun Park, DongJu Lee and Sung Ho Song |
| 저널명 | NANOMATERIALS |
| 게재년월 | 2023. 07. 15 |
| Vol. pp | Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2075 |
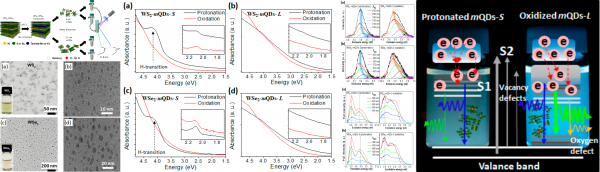
Metallic-phase transition metal dichalcogenide quantum dots (TMDs-mQDs) have been reported in recent years. However, a dominant mechanism for modulating their intrinsic exciton be-haviors has not been determined yet as their size is close to the Bohr radius. Herein, we demonstrate that the oxidation effect prevails over quantum confinement on metallic-phase tungsten dichalco-genide QDs (WX2 -mQDs; X = S, Se) when the QD size becomes larger than the exciton Bohr radius. WX2 -mQDs with a diameter of ~12 nm show an obvious change in their photophysical properties when the pH of the solution changes from 2 to 11 compared to changing the size from ~3 nm. Mean-while, we found that quantum confinement is the dominant function for the optical spectroscopic results in the WX2 -mQDs with a size of ~3 nm. This is because the oxidation of the larger WX2 -mQDs induces sub-energy states, thus enabling excitons to migrate into the lower defect energy states, whereas in WX2 -mQDs with a size comparable to the exciton Bohr radius, protonation enhances the quantum confinement.


 click
click