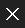An Ultramicroporous Graphene-Based 3D Structure Derived from Cellulos…
페이지 정보
본문
| 논문명 | An Ultramicroporous Graphene-Based 3D Structure Derived from Cellulose-Based Biomass for High-Performance CO2 Capture |
|---|---|
| 저자 | Kwang Hyun Park, Boemjin Ko, Jaegyu Ahn, Taeyoung Park, Soon Do Yoon, Wang-Geun Shim, Sung Ho Song |
| 저널명 | ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces |
| 게재년월 | 2024. 05. 30 |
| Vol. pp | Vol. 16, Issue 23, 30137–30146 |
The use of powered activated carbon is often limited by inconsistent particle sizes and porosities, leading to reduced adsorption efficiencies. In this study, we demonstrated a practical and environmentally friendly method for creating a 3D graphene nanostructure with highly uniform ultramicropores from wood-based biomass through a series of delignification, carbonization, and activation processes. In addition, we evaluated the capture characteristics of this structure for CO2, CH4, and N2 gases as well as its selectivity for binary-mixture gases. Based on textural and chemical analyses, the delignified monolith had a lamellar structure interconnected by cellulose-based fibers. Interestingly, applying the KOH vapor activation technique solely to the delignified samples led to the formation of a monolithic 3D network composed of interconnected graphene sheets with a high degree of crystallinity. Especially, the Act. 1000 sample exhibited a specific surface area of 1480 m2/g and a considerable pore volume of 0.581 cm3/g, featuring consistently uniform ultramicropores over 90% in the range of 3.5−11 Å. The monolithic graphene-based samples, predominantly composed of ultramicropores, demonstrated a notably heightened capture capacity of 6.934 mol/kg at 110 kPa for CO2, along with favorable selectivity within binary gas mixtures (CO2/N2, CO2/CH4, and CO2/CH4). Our findings suggest that this biomass-derived 3D structure has the potential to serve as a monolithic adsorbent in gas separation applications.


 click
click